One might think Mexican immigrants in the U.S. would be sending less money home to their families as a result of the coronavirus.
The 11.2 million people of Mexican origin living in the United States together send upwards of US$38 billion to Mexico each year. This money, called remittances, supports the basic necessities and financial investments of 1.6 million Mexican households – some 10 million people.
In March, analysts at BBVA bank predicted that migrant remittances to Mexico could fall as much as 21% because of stay-at-home orders and record unemployment in the U.S. Instead, remittances reached a record high in early 2020, the Bank of Mexico recently reported. Mexico received $4.02 billion in March 2020, a 35.8% increase over March 2019.
In early May the Mexican president, Andrés Manuel López Obrador, thanked “our migrant countrymen” for sending record remittances in this difficult period, calling them “living heroes.”
How is this possible, when the unemployment rate in the United States is 18.6% and swaths of the American economy are still shut down? My research on remittances finds three reasons.
Immigrants are essential workers
With all the talk of the U.S. economy being “closed,” certain sectors are still going strong – particularly, as the Mexican American community organizers Rodrigo Camarena and Lorena Korusias wrote in City Limits, those staffed by the Mexican workers doing “some of the toughest jobs in our economy.”
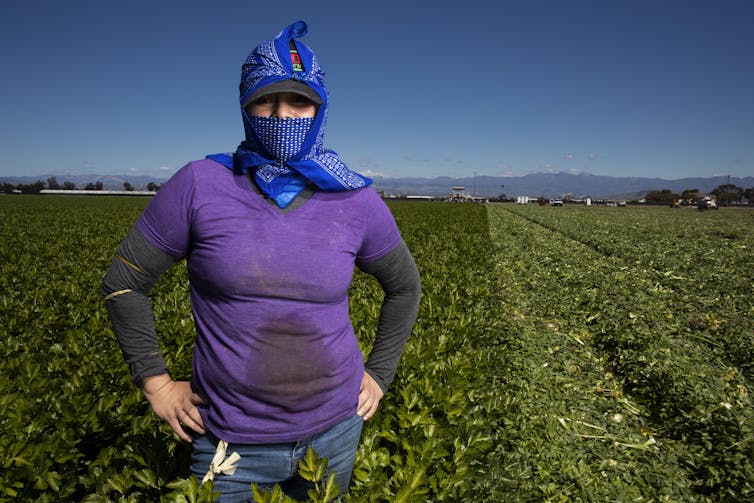
Mexican immigrants are more likely than other workers to be employed in the construction, maintenance, service and production industries, according to U.S. Census data. These are all “essential” sectors of the pandemic economy, though many pay barely above minimum wage.
Employment during this crisis has sustained households that are dependent on every paycheck, both in the United States and back home in Mexico.

Brent Stirton/Getty Images
These jobs – which require people to leave home and interact with other people – have also disproportionately exposed the Latino population to COVID-19. In New York City, the U.S. epicenter of the pandemic, 34% of all COVID-19 fatalities are Mexican or Latino, while Latinos make up just 27% of the city’s population.
As of May 23, 1,036 Mexicans living in the United States had died of the virus, according to the Mexican consular records.
Community advocates attribute the disparate rates of infection and mortality among Latinos to their high-risk working conditions, lack of access to government aid, language barriers and discrimination. These issues are particularly acute for indigenous Mexicans in the U.S.
Exchange rate
The rise in remittances is also due, in part, to a steep decline in the value of the Mexican peso, according to a recent report by the Center for Latin American Monetary Studies, or CEMLA.
In early March, the purchasing power of $1 rose from 19.42 to 25.35 pesos, a 30.5% increase in just three weeks. That means every U.S. dollar sent to Mexico goes farther. During that same time, the CEMLA report says, the average remittance transfer by Mexican migrants in the U.S. increased from $315 to $343.
This particular increase in sending occurred before shelter-in-place orders took effect in major immigration hubs like California and Texas. In the report, CEMLA economic statistics manager Cervantes Gónzalez says migrants took advantage of favorable exchange rates before the economy began closing to maximize their families’ purchasing power.

Luis Sinco/Los Angeles Times via Getty Images
Obligation
On March 23, Mexico began its own gradual shutdown, with the government closing schools, halting many kinds of nonessential business and requiring most people to work from home.
That’s not possible for the estimated 56% of Mexicans who work as domestic laborers, in agriculture and in other informal jobs that lack social security. Their incomes have simply disappeared during the pandemic.
The decline in economic activity in Mexico may have compelled family members working abroad to send more money home, says Gabriela Siller, head economist at Banco BASE, a Mexican bank.
Remittance senders have always felt obligated to their loved ones back home, research shows. It’s likely such feelings of care and responsibility would only increase in a crisis such as COVID-19.
A durable financial relationship
In 2019, the World Bank estimated that global remittances exceeded $550 billion – a massive wealth transfer. And the U.S.-Mexico remittance corridor is one of the world’s most significant, with Mexico being the third-largest receiver of remittances.
So far, it’s also proving to be remarkably durable. Remittances from the U.S. are down in many other Caribbean and Latin American countries.
There’s reason to think cash transfers to Mexico will stay strong. Feelings of familial obligation won’t change due to the pandemic, and the exchange rate between the U.S. dollar and the Mexican peso remains favorable for remittance senders. These factors should keep funds flowing south.
But this financial relationship may still suffer as a result of COVID-19. Soaring unemployment in the U.S. is hitting Latino service workers and small businesses hard, as are COVID-19 infections. Eventually, wage loss and sickness could force even the most loving, responsible and reliable person to send less money back home.
Araby Smyth, Ph.D. Candidate and Instructor in Geography, University of Kentucky
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
One might think Mexican immigrants in the U.S. would be sending less money home to their families as a result of the coronavirus.
The . . .